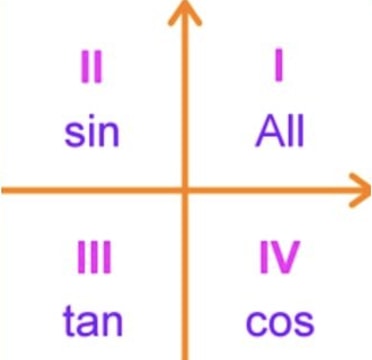
Trigonometric Ratios In Quadrants 2, 3 and 4 Example Determine the exact value of cot 5 4 An angle of 5 4 lies in quadrant 2, with reference angle 4 trigonometry Trigonometric Ratios In Quadrants 2, 3 and 4 Since tangent (and cotangent) is negative in quadrant 2, the exact value will be negative Therefore, cot 5 4 = adj opp = 1Trigonometry Select a subtopic to get started 1^2b^2=2^2\ \1b^2=4\ \3=b^2\ \b=\sqrt{3}\ Both right triangles that are formed by splitting the larger equilateral triangle are equal So Quadrant 3 In this quadrant the angles are between \(180°\) and \(270°\) they are reflex angles Transcript Let s see the angles in different Quadrants In Quadrant 1, angles are from 0 to 90 In Quadrant 2, angles are from 90 to 180 In Quadrant 3, angles are from 180 to 270 In Quadrant 4, angles are from 270 to 360 To learn sign of sin, cos, tan in different quadrants, we remember Add Sugar To Coffee Representing as a table Quadrant I Quadrant II Quadrant III

The Cast Method
Quadrant 1 2 3 4 trigonometry
Quadrant 1 2 3 4 trigonometry-Namaste to all Friends, This Video Lecture Series presented By VEDAM Institute of Mathematics is Useful to all studentSection 43 Trigonometry ExtendedThe Circular Functions Exploration 1 1 The side opposite ¨ in the triangle has length y and the hypotenuse has length r Therefore 2 3 4 cot ¨= ;



What Is All Students Take Calculus In Trig Studypug
Wwwmath30ca Trigonometry LESSON TWO The Unit Circle Lesson Notes a) A circle centered at the origin can be represented by the relation x2 y2 = r2, where r is the radius of the circle Draw each circle i x2 y2 = 4 ii x2 y2 = 49 Example 1 Introduction to Circle Equations (cos f, sin f)1010 1010 1010 10 10 b) A circle centered at the origin with a radius of 1 has theB11, 12 L2 Trig Ratios and Special Angles Determine, without technology, the exact values of trig ratios for special angles B13, 14 L3 Graphing Trig Functions sketch the graphs of all 6 trig ratios and be able to describe key properties B21, 22, 23 L4 Transformations of Trig FunctionsAn Introduction to Trigonometry 18 SECTION 3 SUPPLEMENTARY EXERCISES 1 In a right triangle, if 13 12 nT find the other five trigonometric functions 2 In a right triangle, if 24 7 sT find the other five trigonometric functions 3 In a right triangle, if 2 3 nT find the other five trigonometric functions 4 In a right triangle, if 7 5 nT
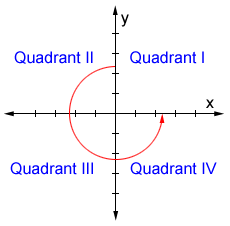
Quadrant I The first quadrant is in the upper righthand corner of the plane Both x and y have positive values in this quadrant Quadrant II The second quadrant is in the upper lefthand corner of the plane X has negative values in this quadrant and y has positive values Quadrant III The third quadrant is in the bottom left cornerTrigonometry Find the Other Trig Values in Quadrant I cos (s)=3/4 cos (s) = 3 4 cos ( s) = 3 4 Use the definition of cosine to find the known sides of the unit circle right triangle The quadrant determines the sign on each of the values cos(s) = adjacent hypotenuse cos (Now try Exercise 1 tan y x 4 3 cos x r 3 5 sin y r 4 5 r x2 y2 3 2 42 25 5 x 3, y 4, 3, 4 y 0, 90 x 0, r x2 y2 Definitions of Trigonometric Functions of Any Angle Let be an angle in standard position with a point on the terminal side of and csc r y sec , y 0 r x, x 0 cot x y tan , y 0 y x, x 0 (, )x y r θ y x cos x r sin y r r x2 y2 0 x
4 S, 3 S, and 2 S, we know the terminal point P Identify the terminal point for the tvalue given and then find the values of the trigonometric functions Ex 1 2 t S sin 2 S cos 2 S tan 2 S cot 2 SCsc ¨= Exploration 2 1 The xcoordinates on the unit circle lie between –1 and 1, and cos t is always an xcoordinate on the unit circle 2 Click anywhere on the quadrant graph demonstration and it will display the point In mathematics, quadrants are commonly labeled with roman numerals, In quadrant i, x is always positive and y is always When the two axes meet, they form four quadrants A horizontal number line in the middle is labeled figure 141




The Cast Method



Trigonometry Trigonometric Functions Functions In Quadrants Sparknotes
Evaluate 6 trig function values x = 1/3 and the radius of unit circle is 1, therefor cos x = 1/3 > x = 70^@53 (Quadrant IV) sin^2 x = 1 cos^2 x = 1 1/9 = 8/9 > sin x = (2sqrt2)/3 Since arc x is in Quadrant IV, then sin x = sqrt2/3 tan x = sin x/(cos x) = (sqrt2/3)(3/1) = sqrt2 cot x = 1/(tan x) = 1/sqrt2 = sqrt2/2 sec x = 1/(cos x) = 3 csc x = 1/(sin x) = 3/(2sqrt2Tan x = 55/23 = 2391 x = tan1 (2391) or x = 6730 degrees Trigonometry Questions Practise these questions given here to get a deep knowledge of Trigonometry Use the formulas and table given in this article wherever necessary Q1 In ABC, rightangled at B, AB=22 cm and BC=17 cm Find (a) sin A Cos B (b) tan A tan BIf necessary, first "unwind" the angle Keep subtracting 360 from it until it is lies between 0 and 360° (For negative angles add 360 instead) Sketch the angle to see which quadrant it is in 2 1 3 4 Depending on the quadrant, find the reference angle Quadrant



Graph Of Y Tan X Video Trigonometry Khan Academy



Higher Maths 1 2 3 Trigonometric Functions
Trigonometry Find the Other Trig Values in Quadrant I csc (x)=4 csc(x) = 4 csc ( x) = 4 Use the definition of cosecant to find the known sides of the unit circle right triangle The quadrant determines the sign on each of the values csc(x) = hypotenuse1 Yes, when the reference angle is π 4 and the terminal side of the angle is in quadrants I and III Thus, at x = π 4, 5π 4, the sine and cosine values are equal 3 Substitute the sine of the angle in for y in the Pythagorean Theorem x2 y2 = 1 Solve for x and take the negative solution 5The others are numbered in counterclockwise order A standard angle whose terminal side lies on the x or yaxis is called a quadrantal angle Quadrantal angles correspond to "integer multiples" of 90 or π
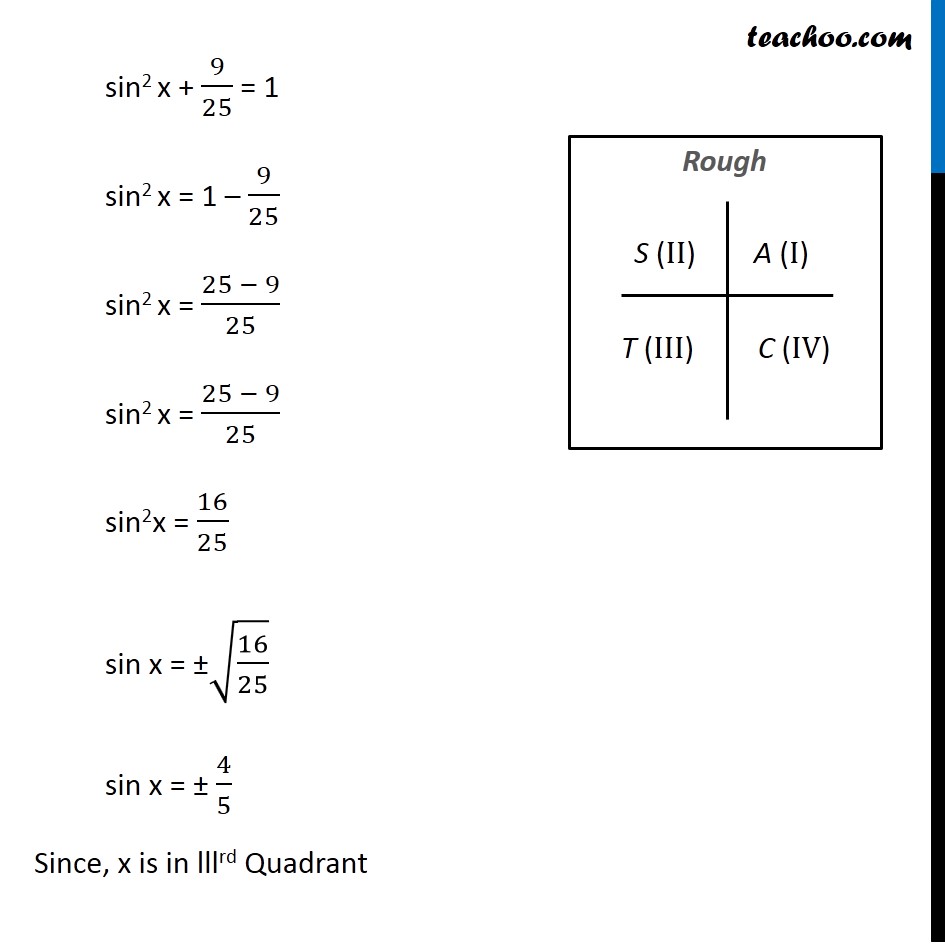



Example 6 If Cos X 3 5 X Lies In Third Quadrant Find
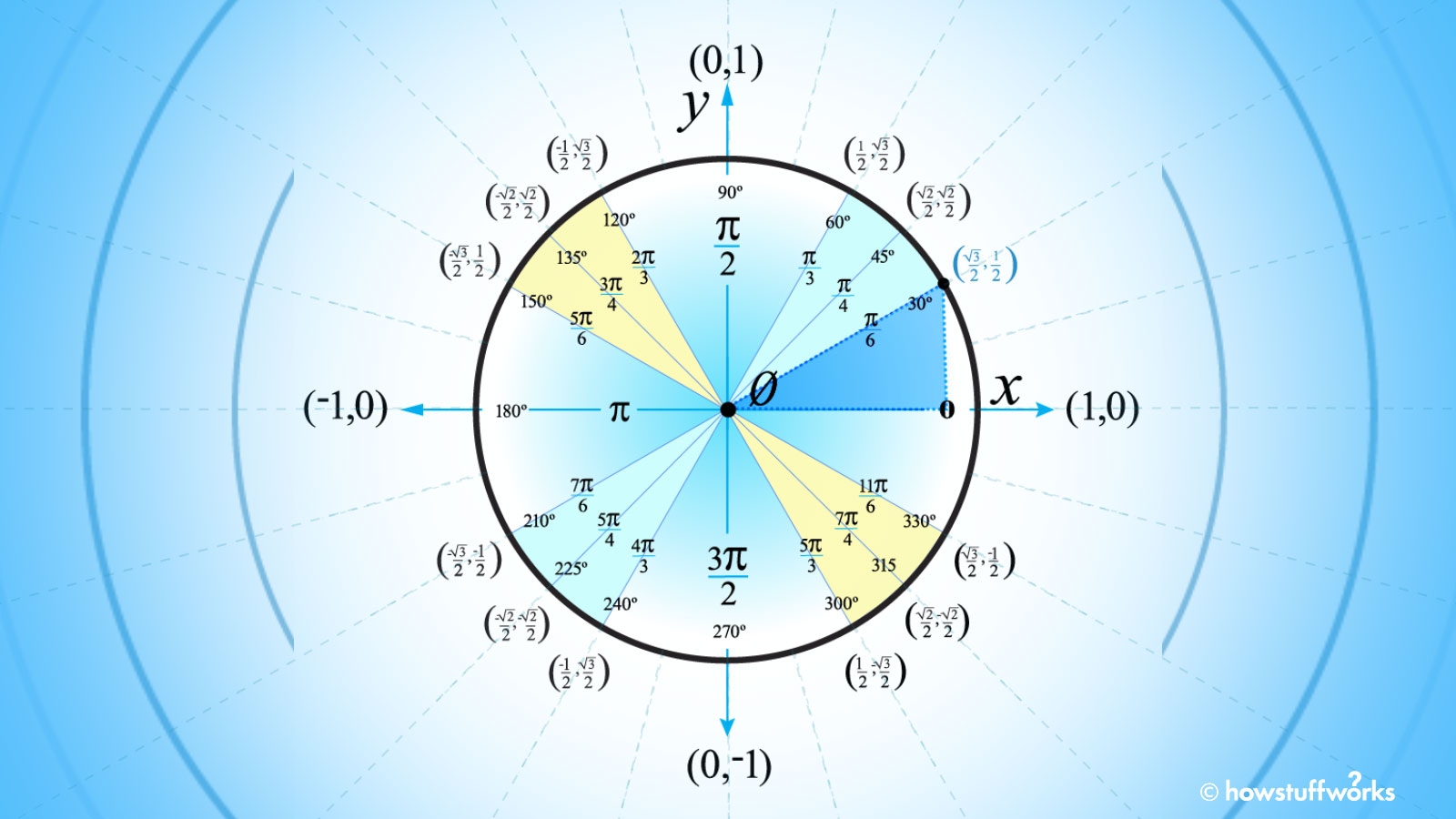



How To Use The Unit Circle In Trig Howstuffworks
Start studying Trig Functions Quadrant 1 Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools405 PART F QUADRANTS AND QUADRANTAL ANGLES The x and yaxes divide the xyplane into 4 quadrants Quadrant I is the upper right quadrant;In quadrant 1, both x and y are positive in value In quadrant 2, x is negative while y is still positive In quadrant 3, both x and y are negative Lastly, in quadrant 4, x is positive while y is negative What this tells us is that if we have a triangle in quadrant one, sine, cosine and



The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl



Trig 02 The Unit Circle Extending Into All 4 Quadrants Youtube
Trigonometry is the study of the relationship between the sides and the angles of triangles the arc length if 2πr /4= 2π(1)/4=π/2 the same as the angle measure, in radians, at that point Reference Angles The right triangle special angles tell us about the sine, cosine, and tangent functions in the first quadrant), s i n7π/6Quadrant System in Trigonometry JEE Main Maths JEE Main 21 Learn Trigonometry Quadrant Rule & Trigonometry Quadrant Formula Class 11 with Neha Ma'am Trigonometry Formulas As the name suggests, trigonometry deals with the study of trianglesThe trigonometry concept includes the use of various trigonometry formulas, identities, and laws Trigonometric identities are used across different areas of work such as engineering architecture, stringed musical instruments and other different scientific specializations




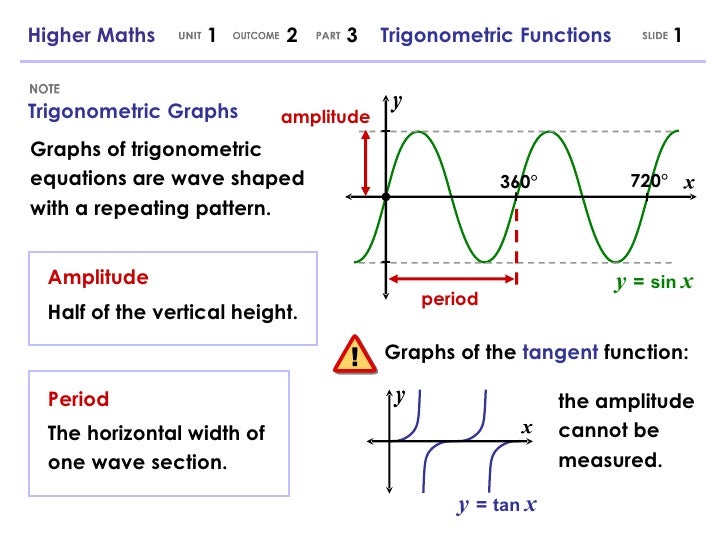
360 Trigonometric Graphs Higher Maths Trigonometric Functions1 Y Sin X Half Of The Vertical Height Amplitude The Horizontal Width Of One Wave Ppt Download




Trigonometric Circle Used To Convert The Angles From Quadrants 2 3 And Download Scientific Diagram
Suppose that the terminal side of angle α lies in Quadrant I and the terminal side of angle β lies in Quadrant IV If sinα=4/5 and cosβ=4/√41, find the exact value of cos(αβ)Unit Circle Trigonometry Learning Objective(s) Understand unit circle, reference angle, terminal side, standard position Find the exact trigonometric function values for angles that measure 30°, 45°, and 60° using the unit circle Find the exact trigonometric function values of any angle whose reference angle measures 30°, 45°, or 60°The value in radians is rounded to 2 decimal places The quadrants are number 1 to 4 and are the quadrant where the angle is in is highlighted in pink Sides The sides are color coded as the diagram below The lengths are normalized to the hypothenuse Hence the hypothenuse is always having a normalized length of 10




How To Solve Trigonometric Equations Using The Quadrant Rule Youtube




4 3 A Trigonometric Ratios Point Px Y
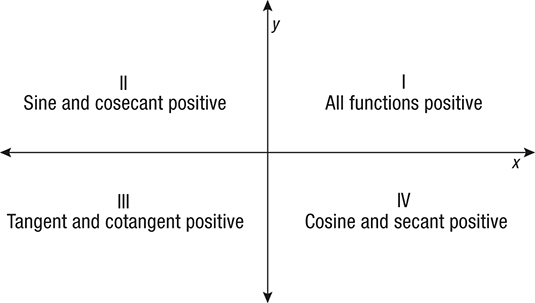
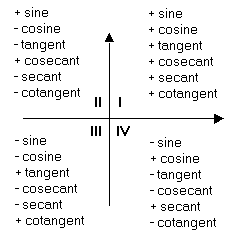
Finally, when angle a is in Quadrant 4 (between 270° and 360°), the adjacent side is back along the positive x direction, while the opposite side is still in the positive y directionHence, Sine and Tangent are negative and only Cosine is positiveTrigonometry Quadrant App Here is a simple interactive app to illustrate the changes in signs of the three basic trigonometry ratios 1 Answer Ken C All the trig functions are positive in Quadrant 1 Sine and cosecant are positive in Quadrant 2, tangent and cotangent are positive in Quadrant 3, and cosine and secant are positive in Quadrant 4Algebra > Trigonometrybasics> SOLUTION If λ is an angle in the second quadrant and sec λ = √85/6 Find the value for cos^4 λ2sin^2 λ cot^3 λ, as a decimal Find the value for cos^4 λ2sin^2 λ cot^3 λ, as a decimal



Quadrant




Unit Circle Memorizing The First Quadrant Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Trigonometry 2 EXAMPLE Find the exact value of sin(u v) given that sin(u) = 1/3 and cos(v) = 3/5, where both u and v are in Quadrant IV Strategy To evaluate sin(u v), we will use the sum formula for sines, sin(u v) = sin(u)cos(v) sin(v)cos(u) To solve for the missing values sin(v) and cos(u), we will use the Pythagorean identity in terms of u and v, ieThe coordinate plane is divided into four regions, or quadrants An angle can be located in the first, second, third and fourth quadrant, depending on which quadrant contains its terminal side When the angle is between and , the angle is a second quadrant angle Since is between and , it is a second quadrant angleUse of calculator to Find the Quadrant of an Angle 1 Enter the angle in Degrees top input example 1250 in Radians second input as a fraction of π Example 27/5 π or 12 π then press the button "Find Quadrant" on the same row If you enter a quadrantal angle, the axis is displayed Example "negative y axis"



Solution One Of The Primary Trigonometric Ratios For An Angle Is Given As Well As The Quadrant That The Terminal Arm Lies In Determine The Other Two Primary Trigonometric Ratios A Sin
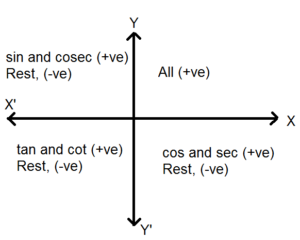



Signs Of Trigonometric Ratios In Diffrent Quadrants Formed Due To Axes
Quadrant I 0° < < 90° = Finding angle when given cos Given that 0° 360°, find when Quad I sign() (a) cos = 0 7660 & Quadrant 2 90° < < 180° SIN () = 180°− Quadrant 3 180° < < 270° TAN () = 180° Quadrant 4 270° < < 360° COS () = 360°− Quad IV a= cos1 0 7660 a = 40°, 360 − 40° = 40°, 3° (b) cos = − 0 5736 sign (−) a= cos1 0 5736 a = 55° = 180° − 551 θ=40D 2 160θ= D 3 θ=−3D Exercises Sketch each of the following angles in standard position (Do not use a protractor;Section 43 Right Triangle Trigonometry 301 first quadrant) and that for such angles the value of each trigonometric function tan 45similar to those in Examples 1, 2, and 3 tan 4 cos 45 cos 1 4 2 2 sin 45 sin 4 2 2 tan 30 tan 6 3 3 cos 30 cos 6 3 2 sin 30 sin 6 1 2 Consider having your students construct



Trigonometric Ratios Solutions Examples Videos




A State The Sign Of Cos T In The Following Interval 3pi 2 2pi B State The Sign Of Cos T In The Following Interval Pi 2 Pi Study Com
Trig Cheat Sheet Definition of the Trig Functions Right triangle definition For this definition we assume that 0 2 p4 = 1 2 = 2 2 csc 𝜋 3 = 2 3 = 23 3 tan30°= 1 3 = 3 3 23 403 Right Triangle Trigonometry ›Sketch a triangle and find 404 Right Triangle Trigonometry and Identities ›Let θbe an acute angle 3 cos 𝜋 3 = 1 2 Quadrant IV where cos is1 31 lies in the fourth quadrant 2 The tangent ratio is negative in the fourth quadrant 3 In the fourth quadrant, the basic acute angle, 360 β = 3600 − 31 = 480 4 Therefore tan 31 = − tan 480 = − (by calculator) Example 4 Given that and is obtuse, find the exact value of Solution Since θ is obtuse, it is in Quadrant 2



1



Trigonometric Functions And The Unit Circle Boundless Algebra
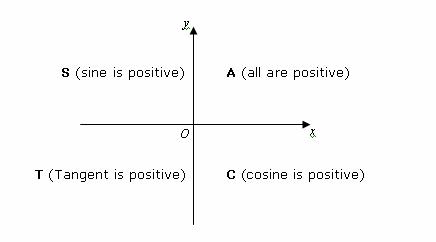
All the trig functions are positive in Quadrant 1 Sine and cosecant are positive in Quadrant 2, tangent and cotangent are positive in Quadrant 3, Angles are shown as central angles in a circle of radius 1 measured in degrees The angle is the complementary angle of , so, for example, the cosine of is the same as the sine of the complementary angle Arc length and coarc length are not "official" trig functions, but for completeness and because they are simple, the author put them in10 r ( x, y) θ O y x Definition 21 Trigonometric Functions of a General Angle Let θ be an angle in standard position and suppose that ( x , y ) is any point other than ( 0 , 0 ) on the terminal side of θ(Figure 23)If r = x2 y2 is the distance between ( x, y ) and ( 0 , 0 ), then the six trigonometric functions of θ are defined by Using similar triangles, you can see that the values




What Is All Students Take Calculus In Trig Studypug
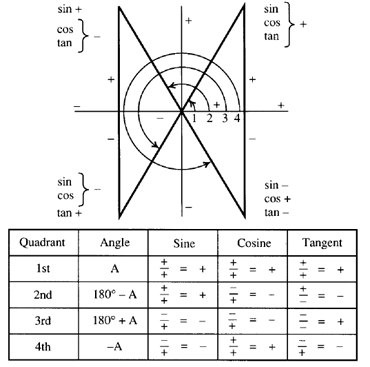



Trigonometric And Geometric Conversions Sin A B Sin A B Sin Ab
Just draw a brief sketch) 1 1θ= D 2 45θ=− D 3 130θ=− D 4 θ=270D θ=−90D 6 θ=750D x y θ Notice that the terminal sides in examples 1 and 3 are in the same position, but they do not represent theCotangent is equal to 1/tangent, which is positive in quadrant 1 and quadrant 3, and negative in quadrant 2 and 4 cosecant is equal to 1/sine, which is positive in quadrant 1 and 2, and negative in quadrant 3 and 4 if the cosecant, which is equal to 1/sine, is negative and the cotangent, which is equal to 1/tangent, is positive, you have to be in quadrant 3 you are given that cosecant theta The tangent function can be though of as the line x=1, where the ray OP is extended to the point T Tangent is only positive in quadrants 1 and 3, and negative in quadrants 2 and 4 Recap ~ Ycoordinate made at the angle ~ Positive where yaxis is positive (quadrants 1, 2) ~ Negative where yaxis is negative (quadrants 3, 4)




Sine Cosine And Tangent In Four Quadrants




Trig Unit Circle Review Article Khan Academy
Given sin A = 5 6 in Quadrant 1, find the exact values of cos A and tan A 2 Solve right triangle ABC (with C = 90 °) given that B = 35 ° and a = 10 Round the sides to two decimal places 3 Solve right triangle ABC (with C = 90 °) exactly given a = 3 and b = 3 √ 3 4 In what two quadrants is sine negative?5 In what two quadrants is
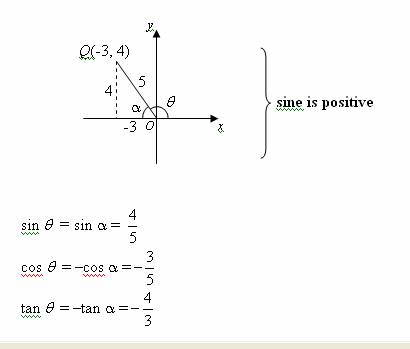



Trigonometric Ratios Solutions Examples Videos




The Unit Circle Ppt Download



If Tan 8 Is Positive And Sin 8 Is Negative In Which Quadrant Does 8 Lie Quora




Sine Cosine And Tangent In Four Quadrants




Relating Trigonometric Functions Ck 12 Foundation



Important Trigonometric Identiti
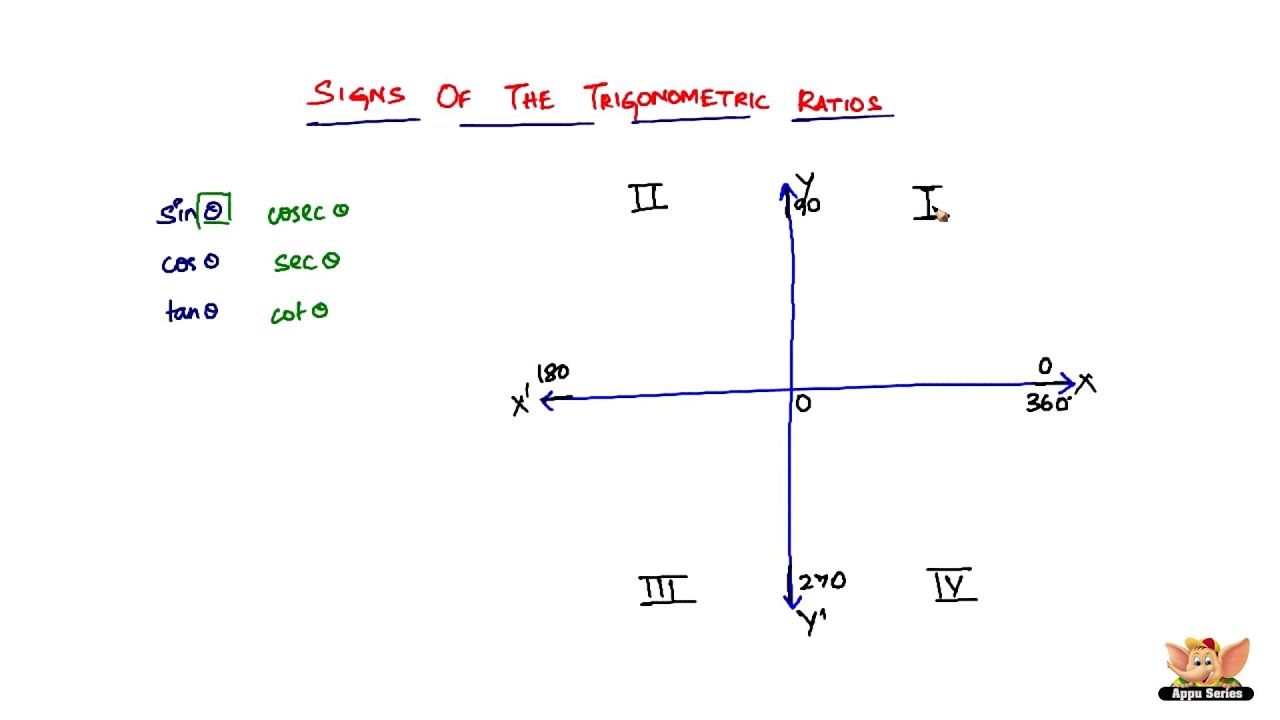



What Are The Sign Conventions Of Trigonometric Ratios In The 4 Quadrants Youtube




Content The Four Quadrants
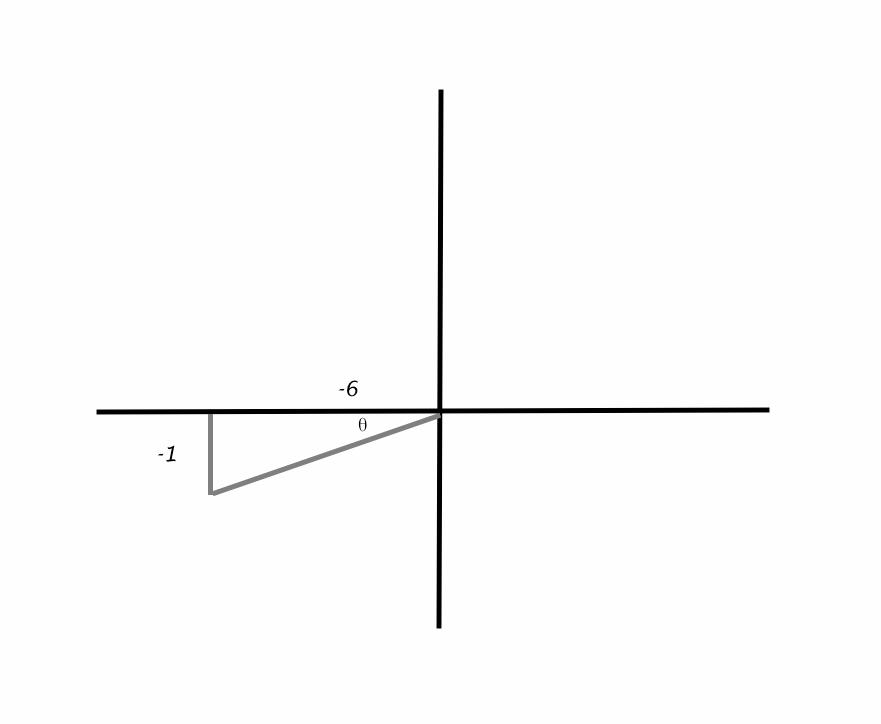



The Terminal Side Of 8 Lies On A Given Line In The Specified Quadrant Find The Values Of The Six Trigonometric Functions Of 8 By Finding A Point On The Line Line




Sine Cosine And Tangent In The Four Quadrants Teachablemath




Chapter 6 Trigonometry Section 6 4 Trigonometric Functions
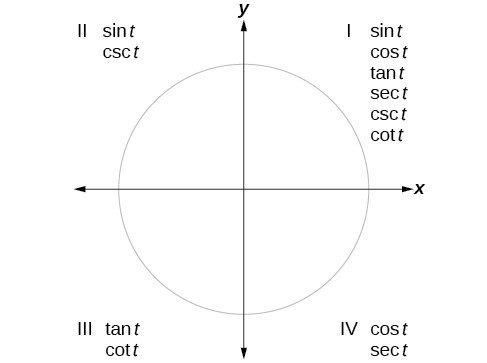



Section 4 4 Reference Angles Precalculus
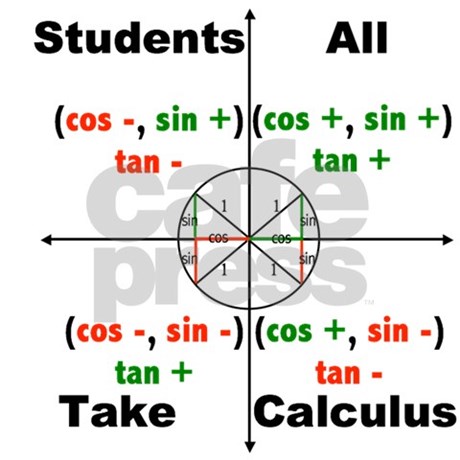



If Cos 0 And Sin 0 What Quadrant Is It In Socratic



1




Sine Cosine And Tangent In Four Quadrants
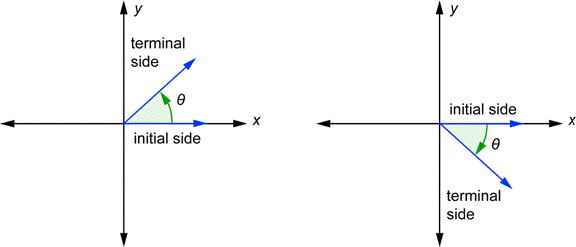



Unit Circle Trigonometry
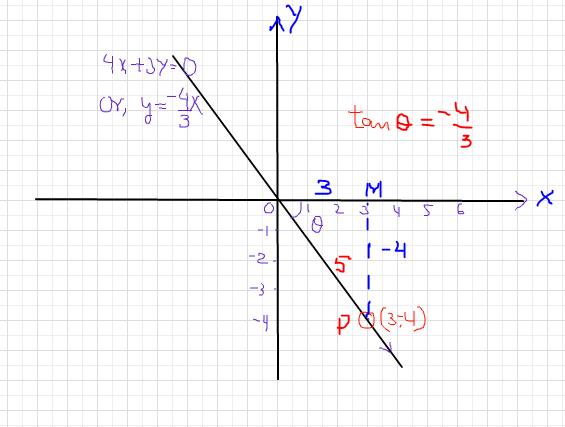



The Terminal Side Of Theta Lies On The Line 4x 3y 0 In Quadrant Iv How Do You Find The Values Of The Six Trigonometric Functions By Finding A Point On The Line




Content The Four Quadrants



1



The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl




Chapter 4 Title Page 4 Lesson Nbsp 3 Primary Trig Ratios Special Angles 2 A To Find




Unit Circle




1 E The Trigonometric Functions Exercises Mathematics Libretexts
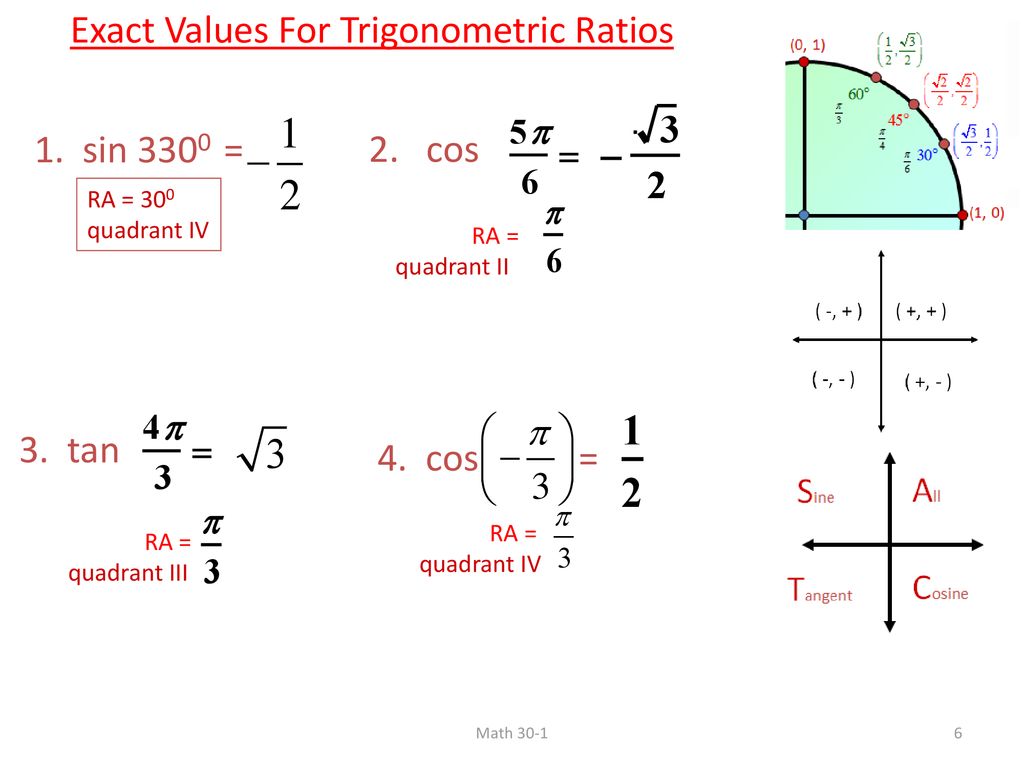



4 3a Trigonometric Ratios Ppt Download
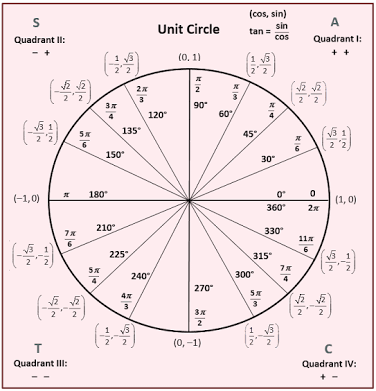



Applying Trig Functions To Angles Of Rotation Trigonometry Socratic
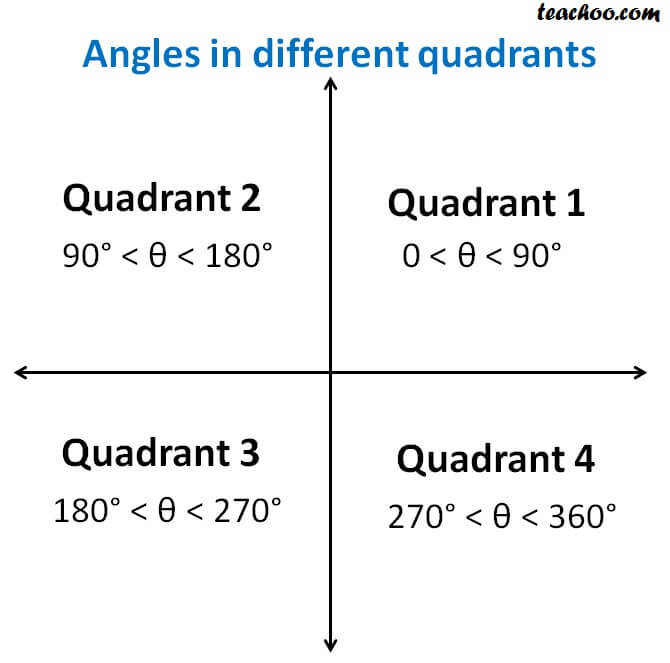



Signs Of Sin Cos Tan In Different Quadrants Finding Value Of Trign




Sine Cosine And Tangent In Four Quadrants




Signs Of Trigonometric Functions




5 8 Defining Ratios In The Cartesian Plane Trigonometry Siyavula



Special Angles In The Unit Circle



What Trig Functions Are Positive In Which Quadrants Socratic



What Trig Functions Are Negative In Quadrant 2 Socratic
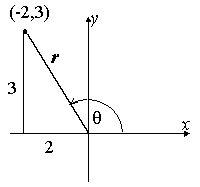



5 Signs Of The Trigonometric Functions




The Trigonometry Functions




Quadrant Plane Geometry Wikipedia



5 Signs Of The Trigonometric Functions



1




Mnemonics In Trigonometry Wikipedia




5 8 Defining Ratios In The Cartesian Plane Trigonometry Siyavula



Quadrant




File Relating Trigonometric Functions Figure 3 Svg Wikimedia Commons
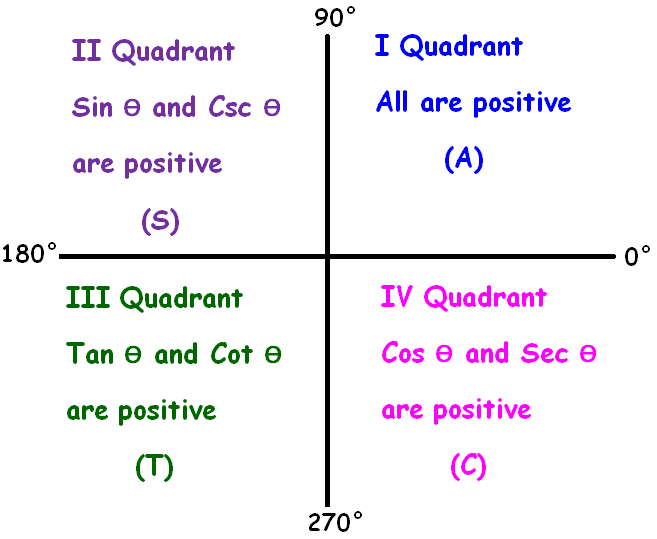



Astc Formula




Trigonometry Facts The Amazing Unit Circle
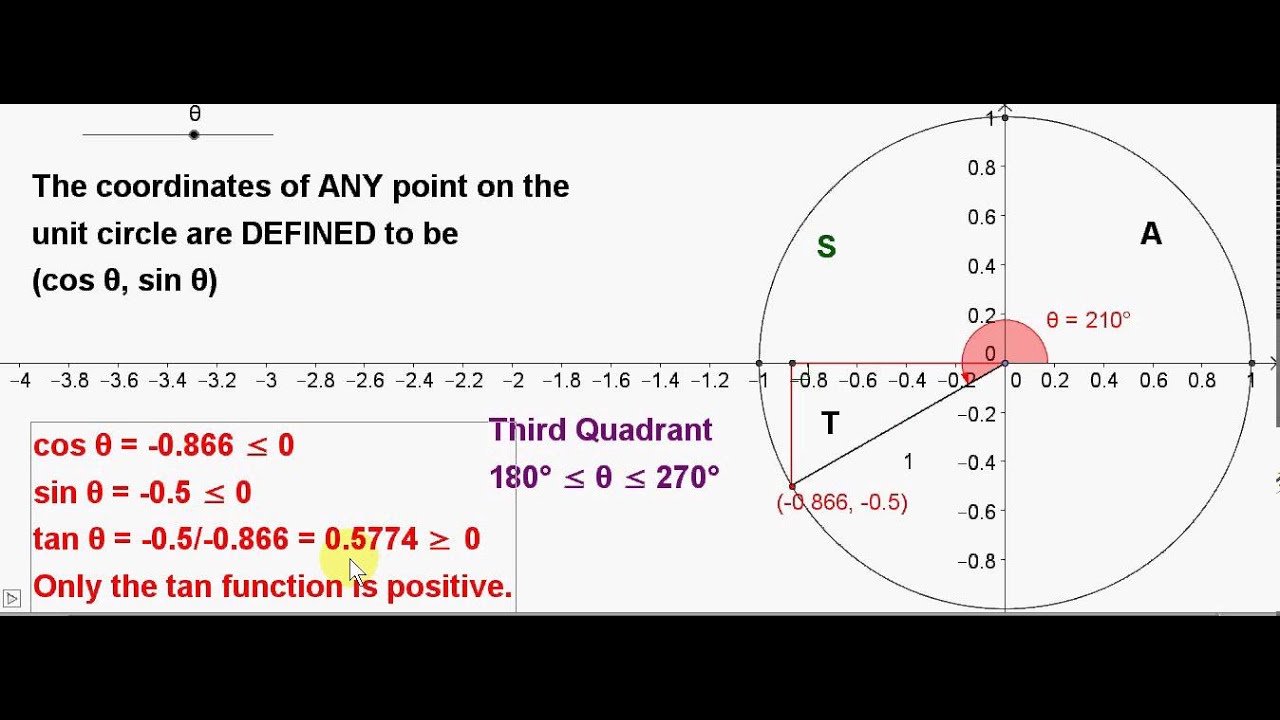



Unit Circle Angles In The Third Quadrant Youtube




Lesson Explainer Signs Of Trigonometric Functions In Quadrants Nagwa
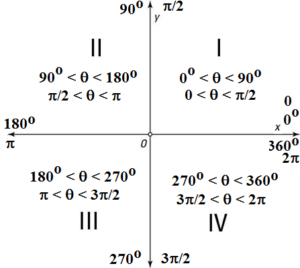



Signs Of Trigonometric Ratios In Diffrent Quadrants Formed Due To Axes




Sine Cosine And Tangent In Four Quadrants



The Point 4 3 Is On The Terminal Arm Of Angle Theta In Standard Position What Are The Primary Trigonometric Ratios Of This Angle Quora




Trigonometry With Any Angle S Cool The Revision Website




Content The Four Quadrants




Trigonometry Facts The Amazing Unit Circle




Sine Cosine And Tangent In Four Quadrants



Cast Rule Mathonline
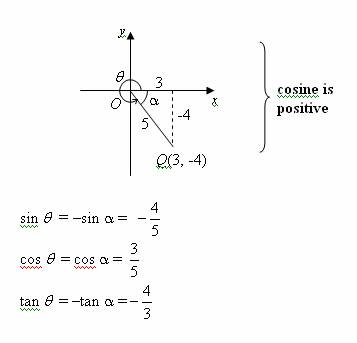



Trigonometric Ratios Solutions Examples Videos
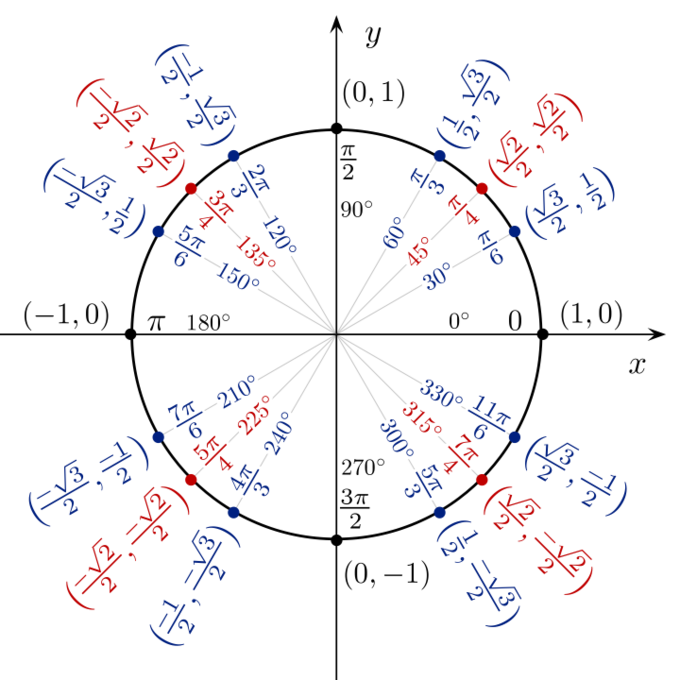



Trigonometric Functions And The Unit Circle Boundless Algebra
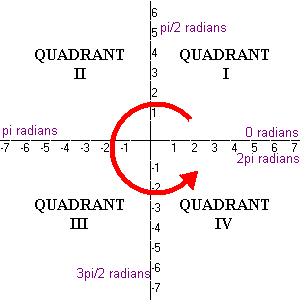



How Do You Determine The Quadrant In Which 6 02 Radians Lies Socratic
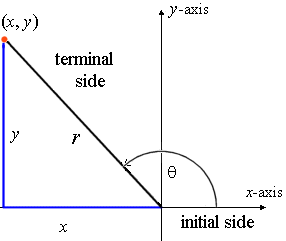



5 Signs Of The Trigonometric Functions
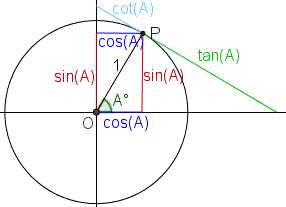



Trigonometry Trigonometric Functions Sin Cos Tan Cot
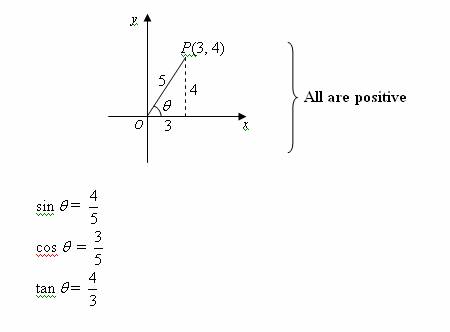



Trigonometric Ratios Solutions Examples Videos
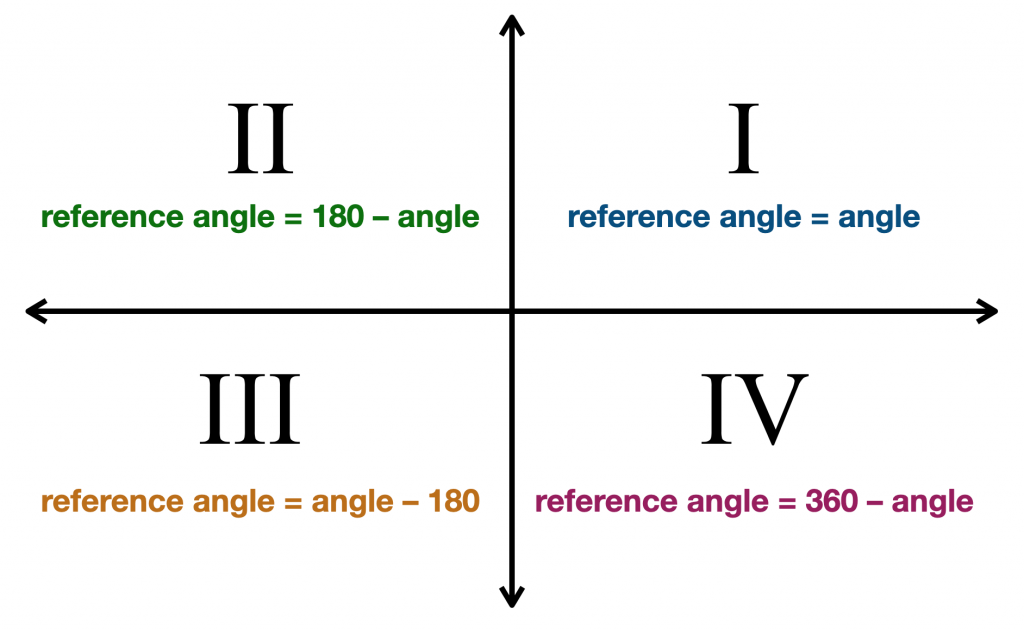



Reference Angle Calculator Pi Day




1 4 Trigonometric Functions Of Any Angle Mathematics Libretexts
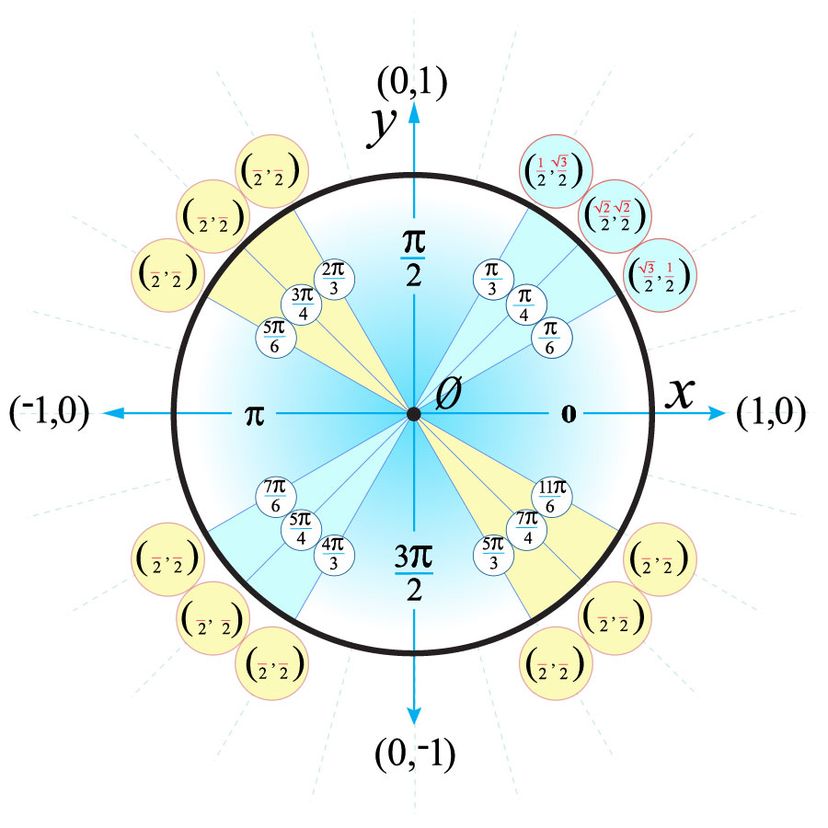



How To Use The Unit Circle In Trig Howstuffworks




Graph Quadrants Examples Definition Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
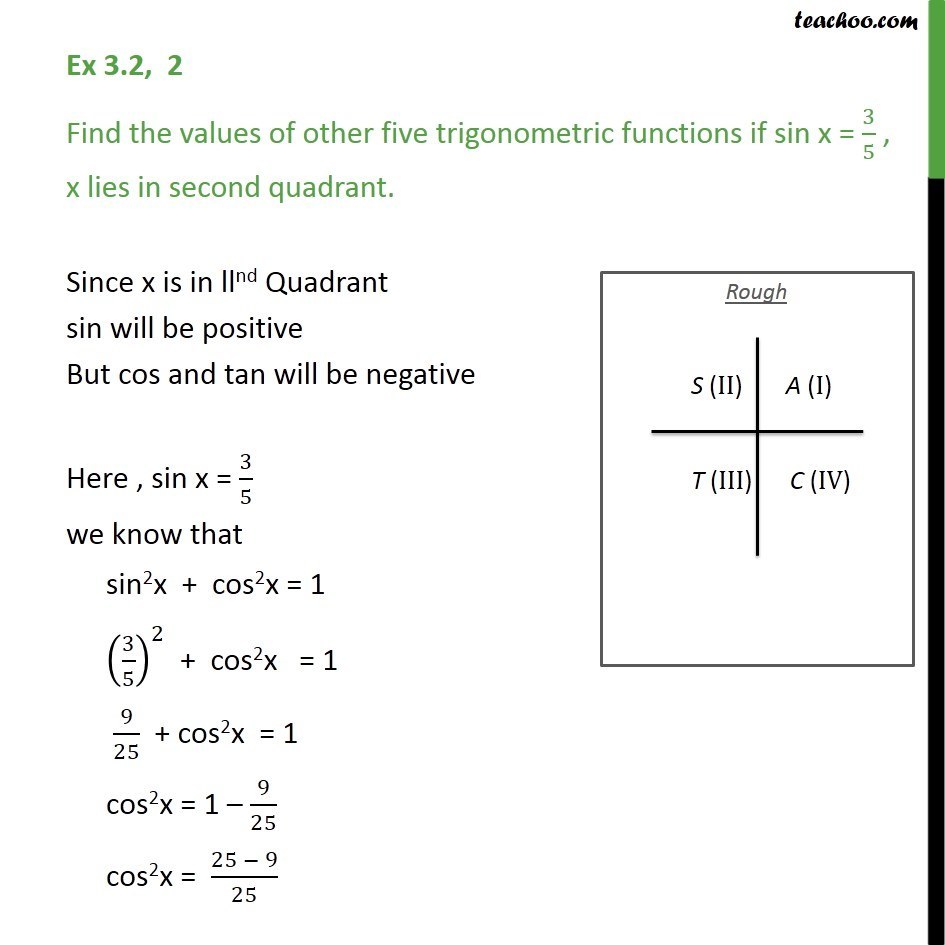



Ex 3 2 2 Find The Values Of Other Five Trigonometric Functions If S




Trigonometry




2 1 Trigonometric Functions Of Non Acute Angles Mathematics Libretexts




Quadrants Trigonometry And Single Phase Ac Generation For Electricians
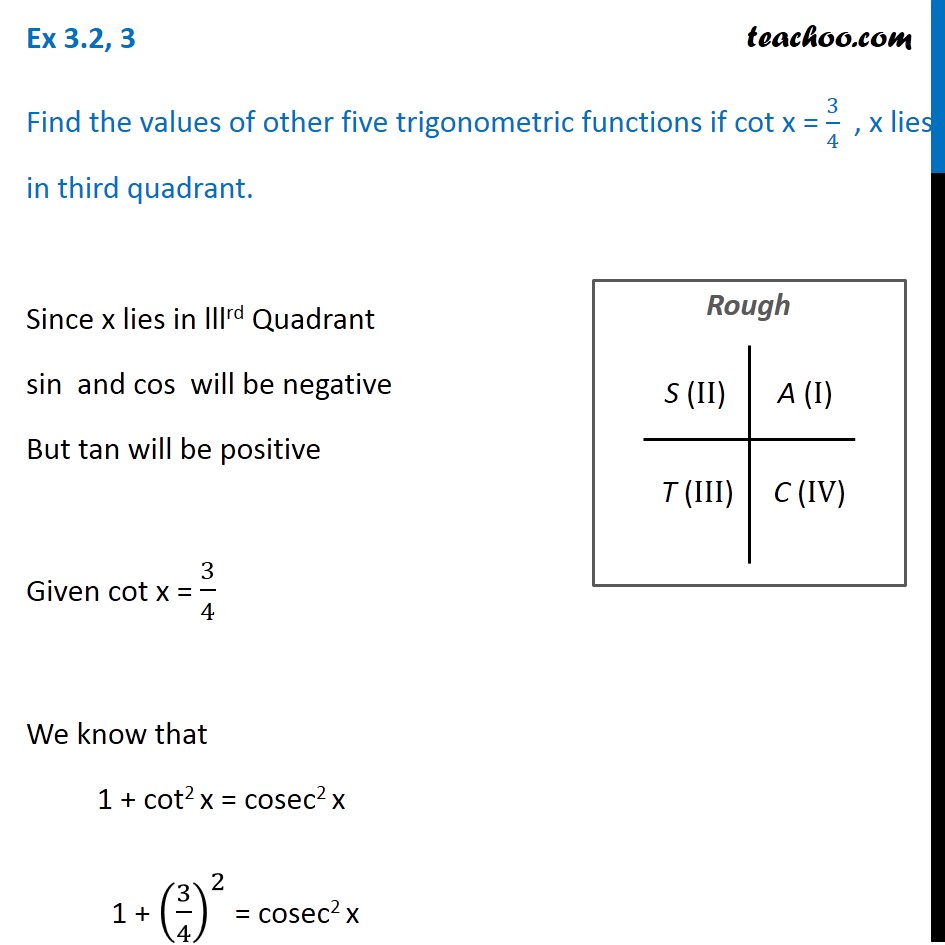



Ex 3 2 3 If Cot X 3 5 Find Values Of Other Trigonometric



File Simple 4 Quadrant Heart Curve Svg Wikimedia Commons



What Is Quadrant Definition Coordinate Graphs Examples Practice Questions




How To Solve Trigonometric Equations Using The Quadrant Rule Youtube



Trigonometry Quadrants And Quadrantal Angles




Quadrant Plane Geometry Wikipedia
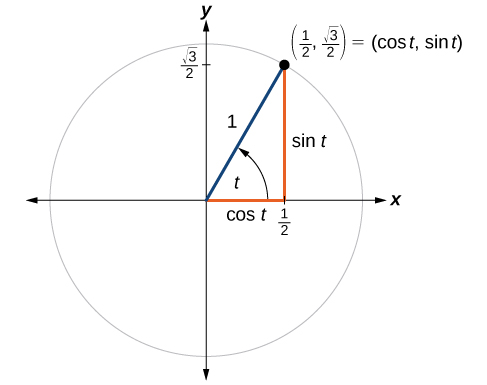



Unit Circle Algebra And Trigonometry




360 Trigonometric Graphs Higher Maths Trigonometric Functions1 Y Sin X Half Of The Vertical Height Amplitude The Horizontal Width Of One Wave Ppt Download
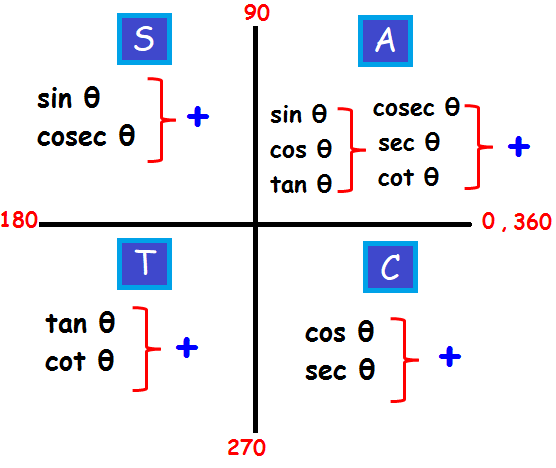



Trigonometry Quadrant Formulas
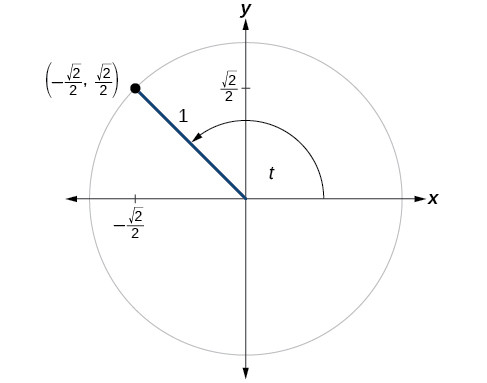



Trigonometric Functions And The Unit Circle Boundless Algebra
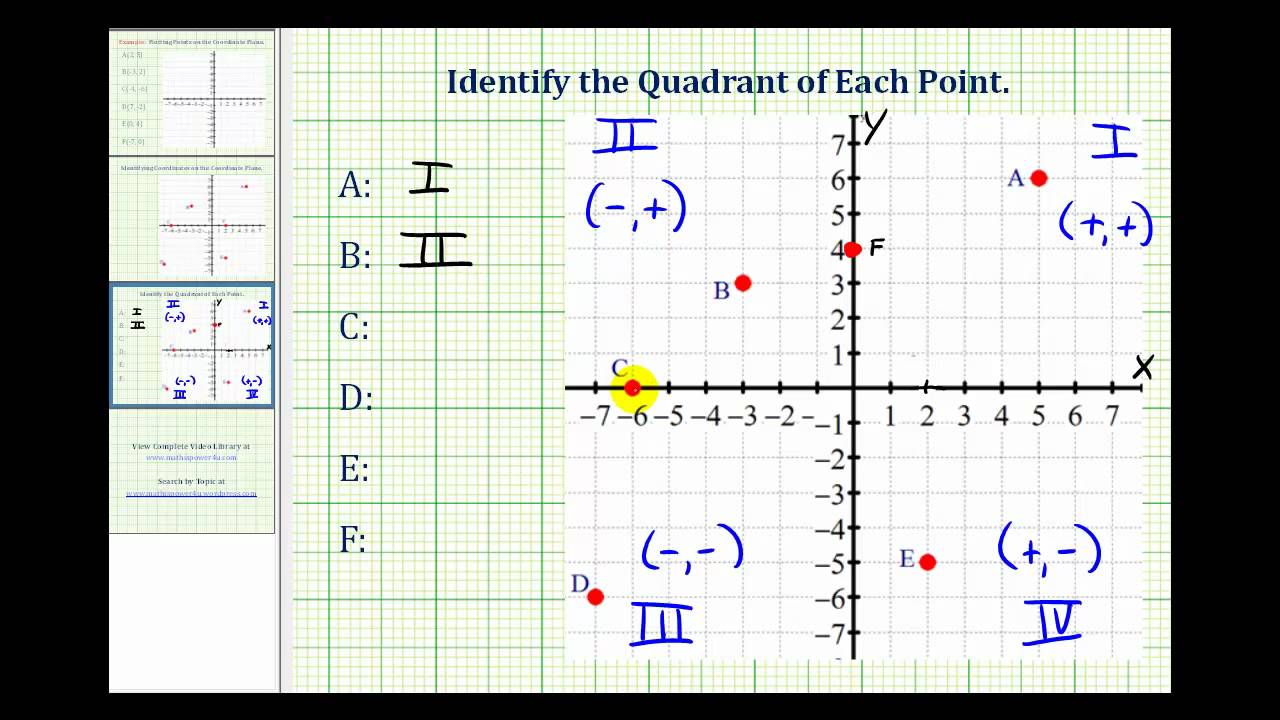



Identify The Quadrant Of A Point On The Coordinate Plane Youtube
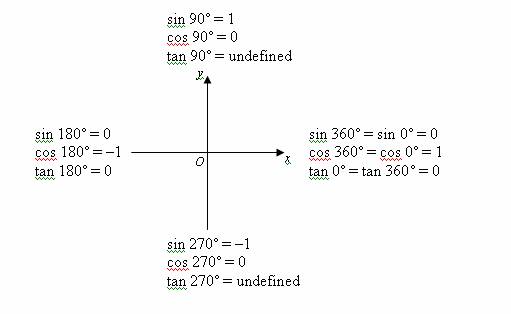



Trigonometric Ratios Solutions Examples Videos



Cast Rule Mathonline



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿